How to Enable VT (Virtualization Technology)?
Reminder: You need to reboot your computer in order to enable Virtualization Technology (VT). We recommend scanning the following QR code to obtain and view the user tutorial on your mobile phone.

Despite being a quite complicated process, enabling VT can significantly boost your gaming experience, and sometimes you even cannot play games normally if it is left disabled. Therefore, please be patient while you overcome this challenge. Keep it up!
I. What is VT? Why to enable it?
Virtualization Technology (VT) is a technology designed to expand hardware capacity. With VT, multiple operating systems can simultaneously run on a platform, and all applications can work within isolated spaces without affecting each other, thereby significantly improving the efficiency of your computer.
Thus, enabling VT can optimize a computer’s mode of operation and boost the performance of the emulator by more than 10 times.
II. How to identity whether VT has been enabled?
If the following reminder (Picture 1) pops up, or the following button is shown on the right corner of the emulator (Picture 2) after the emulator is activated, then VT has not been enabled on your computer. To the contrary, if the button is not displayed, then VT has been enabled.
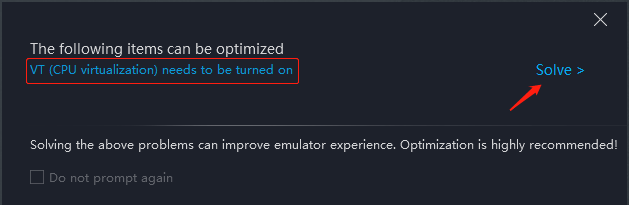
Picture 1:

Picture 2:
III. How to enable VT?
Enabling VT on an ASUS motherboard:
Step 1: Reboot the computer, and press “Del”, or “F2”, or “Fn+F2” repeatedly after the screen turns on to enter the BIOS settings.
Step 2: After accessing to BIOS, click “Advanced Mode”, find the “Intel Virtual Technology” option in “CPU Configuration”, and change the “Disabled” state to “Enabled”.
Step 3: Press “F10” to exit and save changes.
Reminder: The “Intel Virtual Technology” option may not be available on certain models of motherboards. You may find VT settings using key words like “Virtual”, “Virtualization”, “VT-X” and “SVM”.
Enabling VT on a GIGABYTE motherboard:
Step 1: Reboot the computer, and press “Del” repeatedly after the screen turns on to enter the BIOS settings.
Step 2: After accessing to BIOS, open “Chipset”, find the “VT-D” option, and change the “Disabled” state to “Enabled”.
Step 3: Press “F10” to exit and save changes.
Reminder: The “VT-D” option may not be available on certain models of motherboards. You may find VT settings using key words like “Virtual”, “Virtualization”, “VT-X” and “SVM”.
Enabling VT on a Lenovo motherboard:
Step 1: Reboot the computer, and press “F1”, or “Fn+F1”, or “F2”, or “Fn+F2”, or “Del” repeatedly after the screen turns on to enter the BIOS settings.
Step 2: After accessing to BIOS, open the “Advanced” page, find the “Intel(R) Virtualization Technology” option, and change the “Disabled” state to “Enabled”.
Step 3: Press “F10” to exit and save changes.
Reminder: The “Intel(R) Virtualization Technology” option may not be available on certain models of motherboards. You may find VT settings using key words like “Virtual”, “Virtualization”, “VT-X” and “SVM”.
Enabling VT on an MSI motherboard:
Step 1: Reboot the computer, and press “Del”, or “F2”, or “Fn+F2” repeatedly after the screen turns on to enter the BIOS settings.
Step 2: After accessing to BIOS, open the “SETTINGS”-“Advanced”-“Integrated Graphics Configuration” page, find the “Virtu Technology” option, and change the “Disabled” state to “Enabled”.
Step 3: Press “F10” to exit and save changes.
Reminder: The “Virtu Technology” option may not be available on certain models of motherboards. You may find VT settings using key words like “Virtual”, “Virtualization”, “VT-X” and “SVM”.
Enabling VT on a DELL motherboard:
Step 1: Reboot the computer, and press “F2”, or “Fn+F2” repeatedly after the screen turns on to enter the BIOS settings.
Step 2: After accessing to BIOS, if there is “Virtualization Support” option, open it and change the “Disabled” state into “Enabled” in “Virtualization”; if not, you may find the “Virtualization” option and change the “Disabled” state into “Enabled” from “POST Behavior”-“VT”.
Step 3: Press “F10” to exit and save changes.
Reminder: The “Virtualization” option may not be available on certain models of motherboards. You may find VT settings using key words like “Virtual”, “Virtualization”, “VT-X” and “SVM”.
Enabling VT on other motherboards:
Step 1: Identify the model of motherboard in question, and search online for the method to access to its BIOS.
Step 2: After accessing to BIOS, find VT settings using key words like “Virtual”, “Virtualization”, “VT-X” and “SVM”.
Step 3: Press “F10” to exit and save changes.
IV. What if the emulator still reminds that VT is not enabled even it has been activated on the BIOS page?
Situation 1: Possible conflict with some antivirus software. In this case, we recommend you temporarily disable or uninstall your antivirus software and try again.
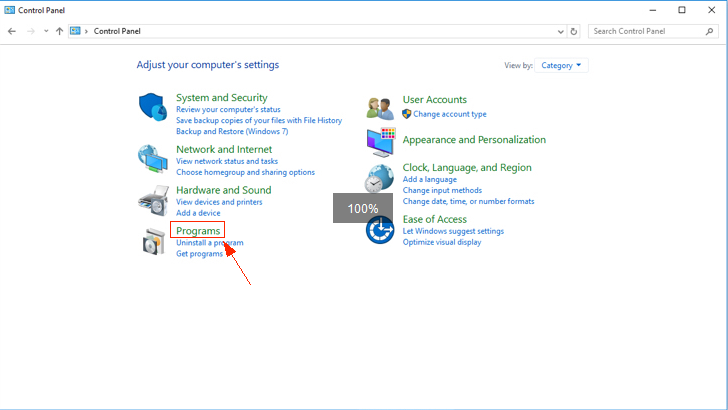
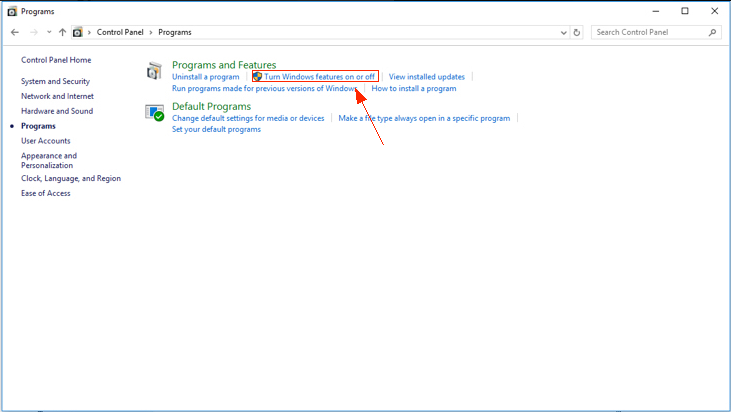
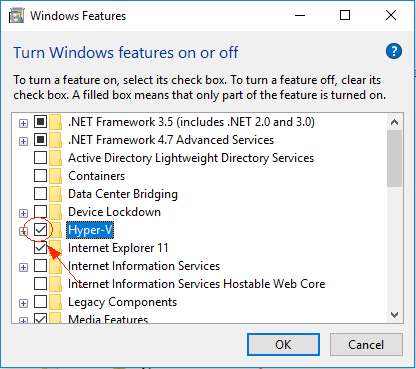
Situation 2: Conflict with “Hyper-V” of Windows 8/Windows 10 operating system. Take Windows 10 as an example: Step 1: Open “Control Panel” and click “Programs”; Step 2: Click “Turn Windows features on or off”. Step 3: Find “Hyper-V” and uncheck the selection, and click “OK” to reboot your computer.
Situation 3: Malfunction of BIOS. We recommend you access to BIOS settings to disable VT, and re-enable it after accessing to the BIOS again.
V. Videos about Enabling VT on Common Motherboards
For Windows 7 users, the following tutorial video is recommended:
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=QE7tZbSwA2Y
For Windows 10 users, the following tutorial video is recommended:
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=-Wa7TGjmn5M
